Introduction
FreeBSD is a powerful and versatile open source operating system that is well suited for a variety of uses, including servers, desktops, and embedded systems. It is known for its advanced networking, security features, and high performance, as well as its easy-to-use system administration tools. Whether you are new to operating systems or are looking for an alternative to more popular options like Linux or Windows, FreeBSD is a great choice for beginners.
The purpose of this article is to guide new users through the process of installing and setting up FreeBSD for the first time. This article covers the prerequisites, installation process, and initial configuration steps, as well as some next steps for continuing your exploration of FreeBSD. By the end of this article, you will have a basic understanding of how to install and configure FreeBSD on your own system.
Brief overview of FreeBSD and why it’s a great operating system for beginners
FreeBSD is a Unix-like operating system that is based on the original Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) code, which was developed at the University of California, Berkeley in the 1970s. Since then, FreeBSD has evolved into a mature and feature-rich operating system that is widely used by businesses, organizations, and individuals around the world.
One of the main reasons that FreeBSD is a great choice for beginners is its ease of use. The operating system is designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, and it comes with a comprehensive manual that covers all aspects of system administration and usage. Additionally, FreeBSD has a strong community of users and developers who are always willing to help new users get started and answer any questions they may have.
Another advantage of FreeBSD is its high performance. The operating system is optimized for modern hardware and is designed to run quickly and efficiently, even on older systems. This makes it a great choice for use as a server or desktop system, as well as for use in embedded systems where performance and reliability are critical.
Finally, FreeBSD is known for its advanced networking and security features. The operating system provides robust support for a wide range of networking protocols, including TCP/IP, IPv6, and others, and it also includes a number of security features that help to protect against security threats and attacks. Whether you are setting up a network or just want to ensure the security of your personal computer, FreeBSD is a great choice for beginners.
The purpose of the article: to guide new users through the installation and initial setup process
The installation and initial setup of an operating system can be a daunting task, especially for those who are new to using computers or who have never installed an operating system before. This article is designed to make the process as easy and straightforward as possible, by guiding new users through each step of the process.
The article covers the prerequisites for installing FreeBSD, such as downloading the installation image and ensuring that your computer meets the minimum hardware requirements. It also covers the installation process itself, including booting from the installation media, partitioning the hard drive, and configuring the network. Finally, the article covers the initial configuration steps, such as setting the root password, creating a new user account, and updating the system.
By the end of this article, you will have a basic understanding of how to install and configure FreeBSD on your own system. You will also have a good foundation for exploring the operating system further and learning about its advanced features and capabilities. Whether you are setting up a server, a desktop, or an embedded system, this article will help you get started with FreeBSD.
Prerequisites
Before you begin the installation process for FreeBSD, there are a few prerequisites that you should be aware of. These include downloading the installation image, ensuring that your computer meets the minimum hardware requirements, and creating a bootable installation media.
- Download the Installation Image: The first step is to download the latest version of FreeBSD from the official website (www.freebsd.org). The installation image is available in both ISO and USB format, and you should choose the format that is best suited to your needs.
- Check Hardware Requirements: Before installing FreeBSD, you should ensure that your computer meets the minimum hardware requirements. These requirements include a 32-bit or 64-bit processor, at least 64MB of RAM, and a hard drive with a minimum of 1.5GB of free space. You can find the full list of hardware requirements on the FreeBSD website.
- Create Bootable Installation Media: Once you have downloaded the installation image, you need to create a bootable installation media. This can be done by burning the ISO image to a CD or DVD, or by writing the USB image to a USB drive using a tool such as dd.
By completing these prerequisites, you will be ready to begin the installation process for FreeBSD. In the next section of this article, we will cover the steps involved in installing the operating system on your computer.
Minimum hardware requirements
Before installing FreeBSD, it’s important to ensure that your computer meets the minimum hardware requirements. This will ensure that the operating system will run smoothly and efficiently on your system.
The hardware requirements for minimum FreeBSD installations are:
- A 32-bit or 64-bit processor
- 64 MB of RAM
- A hard drive with a minimum of 1.5 GB of free space
- A CD or DVD drive, or a USB port for booting the installation media
In addition to these requirements, it is also recommended that you have a keyboard, mouse, and display for the installation process, as well as an Internet connection for downloading updates and additional software packages.
If you’re unsure whether your computer meets the minimum hardware requirements for FreeBSD, you can check the specifications of your computer or consult with a technical expert.
It’s important to note that these minimum requirements are for a basic installation of FreeBSD, and you may need additional resources if you plan to run a server or use the operating system for more demanding tasks. However, for most beginners, these minimum requirements will be sufficient for getting started with FreeBSD.
Downloading the installation image
The first step in installing FreeBSD is to download the latest version of the operating system. You can download the installation image from the official FreeBSD website (www.freebsd.org).
The installation image is available in two formats: ISO and USB. The ISO format is a traditional CD or DVD image, while the USB format is a bootable image that can be written to a USB drive. You should choose the format that is best suited to your needs.
If you choose the ISO format, you will need to burn the image to a CD or DVD, while if you choose the USB format, you will need to write the image to a USB drive using a tool such as dd.
Once you have downloaded the installation image, you are ready to move on to the next step in the installation process, which is creating a bootable installation media. Before proceeding, it is important to verify the integrity of the image to ensure that it has not been tampered with and is safe to use. You can do this by checking the checksum of the image, which is provided on the FreeBSD website.
By downloading the installation image, you are one step closer to installing FreeBSD on your computer and experiencing the benefits of this powerful and flexible operating system.
Installation Process
With the installation image and bootable installation media ready, you are now ready to start the installation process for FreeBSD. The installation process is straightforward and easy to follow, and can be done in a few simple steps.
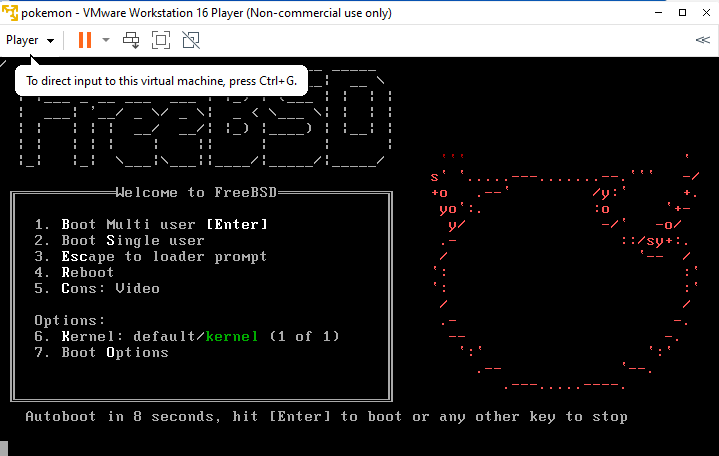
Boot from installation media
The first step in the installation process is to boot from the installation media. To do this, insert the bootable installation media into your computer and restart the machine.
In the boot menu, select the option to boot from the CD/DVD or USB drive, depending on the format of your installation media. The boot menu is usually accessed by pressing a key such as F12 or Esc during the boot process.
Once you have selected the option to boot from the installation media, the FreeBSD boot menu will be displayed. From here, you can choose to start the installation process, run the live environment, or perform other tasks such as checking the integrity of the installation media or using the rescue system.
It’s important to select the option to start the installation process, as this will take you to the next step in the installation process, where you will select the keyboard layout for the installation.
By booting from the installation media, you are starting the process of installing FreeBSD on your computer and experiencing the benefits of this powerful and flexible operating system.
If you encounter any issues booting from the installation media, such as the boot menu not appearing, you can consult the official FreeBSD documentation or seek help from the FreeBSD community for assistance.
Partitioning the hard drive
After selecting the keyboard layout for the installation, the next step in the installation process is to partition the hard drive for the installation of FreeBSD. This step is important because it determines how the operating system and its files will be organized on your computer.
There are two options for partitioning the hard drive: automatic and manual.
- Automatic Partitioning: If you choose the automatic partitioning option, the installation process will automatically create a partition for FreeBSD and allocate the necessary space for the operating system and its files. This option is recommended for beginners who are not familiar with partitioning and want to get up and running quickly.
- Manual Partitioning: If you choose the manual partitioning option, you will have more control over how the hard drive is partitioned and how much space is allocated to each partition. This option is recommended for advanced users who have specific requirements for their partitioning scheme.
Once you have chosen the partitioning option that best suits your needs, you can proceed with the installation process. The partitioning process may take a few minutes, depending on the size of your hard drive, so be patient and allow the process to complete.
After the partitioning process is complete, you can begin the process of installing the operating system, which will be covered in the next section of this guide.
It’s important to note that partitioning the hard drive correctly is crucial to the stability and performance of your operating system, so take care to choose the appropriate option for your needs and follow the steps carefully. If you encounter any issues during the partitioning process, you can seek help from the FreeBSD community or consult with a technical expert.
Installing the operating system
After partitioning the hard drive, the next step in the installation process is to install the operating system itself. This step involves copying the necessary files from the installation media to the hard drive and configuring the operating system to work with your computer’s hardware.
The installation process is straightforward and easy to follow, with clear instructions provided on the screen at each step. Some of the key steps in the installation process include:
- Selecting the partition to install FreeBSD: In this step, you will be asked to select the partition that was created during the partitioning process. Make sure to select the correct partition and verify that the correct amount of disk space is allocated to it.
- Setting the root password: In this step, you will be asked to set a password for the root user. The root user is the administrator of the operating system and has full access to all the system resources. Make sure to choose a strong and secure password.
- Configuring the network: In this step, you will be asked to configure your network settings, including the hostname, IP address, netmask, and default gateway. This information is necessary for your computer to communicate with other devices on your network.
- Installing the system: In this step, the operating system files will be copied from the installation media to your hard drive and the necessary configurations will be made to make the system ready for use. This step may take several minutes, so be patient and allow the process to complete.
After the operating system has been installed, you can remove the installation media and restart your computer to boot into the newly installed FreeBSD system.
The installation process is simple and straightforward, but if you encounter any issues during the installation, you can seek help from the FreeBSD community or consult with a technical expert.
Congratulations! You have now successfully installed FreeBSD on your computer and are ready to start exploring the many features and capabilities of this powerful and flexible operating system.
Setting the root password
The root account is the most powerful account on your FreeBSD system and should be protected by a strong password. By default, the root password is not set, so it’s important to set a password for this account during the installation process.
As soon as the operating system files are installed, you will be prompted to enter root password.
It’s important to choose a strong password that is difficult to guess or crack. You should use a combination of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols to create a secure password.
In conclusion, setting the root password is an important step in securing your FreeBSD system and ensuring that your data is protected. By following these simple steps, you can set a strong password for the root account and get started using your new operating system.
Configuring the network
One of the important steps in the initial setup process is configuring the network settings on your computer. This step is necessary for your computer to communicate with other devices on your network, as well as access the internet.
FreeBSD provides several options for configuring the network, including DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) and manual configuration.
- DHCP Configuration: If you choose the DHCP option, your computer will automatically obtain an IP address, netmask, and default gateway from a DHCP server on your network. This option is recommended for beginners who do not have specific network requirements and want to get up and running quickly.
- Manual Configuration: If you choose the manual configuration option, you will be asked to enter the necessary information, such as the IP address, netmask, and default gateway, manually. This option is recommended for advanced users who have specific network requirements and want more control over their network configuration.
Regardless of which option you choose, it’s important to verify that the network is configured correctly and that you can connect to other devices on your network and access the internet. You can use the “ping” command to test the network connectivity, and if you encounter any issues, you can seek help from the FreeBSD community or consult with a technical expert.
In addition to configuring the network, it’s also a good idea to configure the firewall on your computer to ensure the security and privacy of your network. FreeBSD provides several options for configuring the firewall, including IPFW (IP Firewall), PF (Packet Filter), and IPF (IP Filter).
By configuring the network and firewall, you can ensure that your computer is connected to your network and that it is secure and protected from potential security threats.
Initial Configuration
After successfully installing the operating system, it’s time to configure the system to meet your specific needs and requirements.
Creating a new user account
In addition to the “root” account, it’s also a good idea to create a separate user account for everyday use. This will help you to keep your work and personal files separate, and it will also make it easier to manage permissions and access to files and resources.
To create a new user account, follow these steps:
- Log in as the “root” user.
- Use the “adduser” command: To create a new user account, use the “adduser” command and follow the prompts to enter the user’s information, including the username, password, and home directory.
- Set the user’s permissions: You can set the user’s permissions by using the “chmod” command to change the permissions on the user’s home directory.
- Log in as the new user: You can log in as the new user by logging out of the “root” account and logging in using the new username and password.
It’s important to choose a strong password for the new user account, just as you did for the “root” account. You should also choose a unique username that is easy to remember and that is not already in use by another user on the system.
In conclusion, creating a new user account is a simple process that will help you to manage your files and resources more effectively and securely. By following these steps, you can create a new user account on your FreeBSD system and start using it for your everyday computing needs.
Updating the system
It’s important to keep your FreeBSD system up to date with the latest security patches and software updates. Updating the system is a simple process that can be done using the “freebsd-update” command for the operating system.
To update the operating system, follow these steps:
- Log in as a privileged user: To update the system, you will need to log in as a user with administrative privileges, such as the “root” user or a user in the “wheel” group and use “su” command.
- Downlaod the updates for the current operating system: Before you can install the new operating system files, you need to download the differences and apply patches with “freebsd-update fetch” command.
- Install the updates: Once the differences are ready in the local system, those files can be installed with “freebsd-update install” command.
- Restart the system: Restarting the system is not mandatory if kernel files are not updated. But it’s a good idea to restart the system to ensure that all changes are properly applied.
It’s important to keep your system up to date in order to ensure that it is secure and functioning optimally. By following these simple steps, you can keep your FreeBSD system up to date and enjoy all of its features and benefits.
In conclusion, updating the system is a critical task that helps to keep your FreeBSD system secure and functioning smoothly. By following these steps, you can keep your system up to date and enjoy all of the latest software and security updates.
Installing basic software and tools
Once you have installed and set up your FreeBSD system, you will likely want to install some basic software and tools to help you get started. There are many options available, ranging from text editors and development tools to desktop environments and multimedia applications.
To install basic software and tools, follow these steps:
- Log in as a privileged user: To install software, you will need to log in as a user with administrative privileges, such as the “root” user or a user in the “wheel” group and use “su” command.
- Use the “pkg” package manager: To install software and tools, you can use the “pkg” package manager, which is included with your FreeBSD system.
- Search for packages: To find the packages that you want to install, you can use the “pkg search” command to search the package repository for specific software or tools.
- Install packages: Once you have found the packages that you want to install, you can use the “pkg install” command to install them. You may also need to install additional dependencies or libraries to run certain software.
- Update the PATH environment variable: After you have installed new software, you may need to update the PATH environment variable to ensure that the software is accessible from the command line.
It’s important to choose software and tools that are compatible with your FreeBSD system, and to carefully read and follow the instructions for installing and configuring the software. By doing so, you can install and use basic software and tools on your FreeBSD system and start to get the most out of your new operating system.
In conclusion, installing basic software and tools is a simple process that can help you to get the most out of your FreeBSD system. By following these steps, you can install and use the software and tools that you need to be productive and enjoy your new operating system.
Next Steps
Now that you have installed and set up your FreeBSD system, there are many more things that you can do to get the most out of your new operating system. Here are some next steps that you can consider:
Understanding FreeBSD’s directory structure
One of the first things that new users of FreeBSD should understand is the structure of the file system. Unlike other operating systems, which often use a hierarchical file system structure, FreeBSD uses a unified file system that combines all of the files and directories into one cohesive tree structure. Here is a brief overview of the most important directories that you should know:
- /root: This directory contains the home directory of the root user, and is where the system administrator can manage the configuration files and perform administrative tasks.
- /usr: This directory contains the majority of the user-level applications, libraries, and documentation. It is where most of the software that you will install will reside.
- /var: This directory contains files that change frequently, such as log files, temporary files, and databases.
- /etc: This directory contains configuration files for the operating system and installed applications.
- /bin: This directory contains the essential command-line utilities that are used by both the system and the users.
- /sbin: This directory contains the system administration commands that are used by the system administrator to manage the system.
- /tmp: This directory contains temporary files that are generated by the system and the users.
- /dev: This directory contains the device files that represent the system’s hardware and peripherals.
- /usr/local: This directory contains all files which is installed by “pkg” command. So we can identify if they are base OS files or application files easily.
By understanding the structure of the file system, you can quickly navigate to the relevant files and directories, and perform various administrative and management tasks more effectively. Furthermore, it will be easier for you to understand the output of various commands and logs, as well as the location of installed software and their configuration files.
Configuring the system for use
Now that you have completed the initial setup and installation of FreeBSD, it’s time to configure the system to meet your specific needs. Here are some key steps to take:
- Configure the network: Ensure that your network connection is working correctly and that the IP address, netmask, and default gateway are set correctly. You can do this using the “ifconfig” and “route” commands.
- Install additional software: Depending on your use case, you may need to install additional software, such as web servers, databases, or programming languages. You can use the “pkg” command to install packages from the FreeBSD package repository.
- Configure the firewall: If you need to secure the system from external threats, you can configure the firewall to restrict incoming and outgoing network traffic. You can use the “ipfw” command to configure the firewall.
- Set up SSH access: If you want to access the system remotely, you can set up secure shell (SSH) access. This will allow you to log in to the system from another computer and perform administrative tasks. You can use the “sshd” command to start the SSH daemon.
- Customize the environment: You can customize the environment to meet your specific needs by configuring the shell, installing additional software, and modifying the system configuration files.
By following these steps, you will have a fully functional and secure FreeBSD system that is ready for use. Whether you are using the system as a personal desktop, a web server, or a development environment, these steps will help you get the most out of your new operating system.
Joining the FreeBSD community
FreeBSD is a thriving open-source community with a wealth of resources and support available to new users. Here are some ways to get involved and take advantage of the community:
- Join the mailing list: The FreeBSD mailing list is a great place to get answers to your questions and connect with other users. You can join the list by visiting the FreeBSD mailing list page and subscribing to the relevant list for your area of interest.
- Participate in forums: There are several forums dedicated to FreeBSD where you can ask questions, get advice, and connect with other users. Some popular forums include the FreeBSD forums and the Reddit FreeBSD subreddit.
- Attend events: FreeBSD events such as conferences, meetups, and workshops provide opportunities to meet other users, learn new skills, and get involved in the community. You can find a list of upcoming events on the FreeBSD events page.
- Contribute to the project: One of the best ways to get involved in the FreeBSD community is to contribute to the project. Whether you’re a developer, tester, writer, or designer, there are many ways to get involved and make a difference. You can find more information on how to contribute on the FreeBSD volunteer page.
By getting involved in the FreeBSD community, you will have the opportunity to learn new skills, connect with other users, and contribute to the development and success of the operating system. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, the community is a great resource for information, support, and collaboration.
Conclusion
In this article, we have provided a comprehensive guide for installing and setting up FreeBSD. We have covered the various steps involved, including downloading the installation image, booting from the installation media, partitioning the hard drive, configuring the network, setting the root password, creating a new user account, updating the system, and installing basic software and tools.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you will be able to get up and running with FreeBSD quickly and easily. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, FreeBSD offers a wealth of features and capabilities that make it a great choice for a wide range of applications and uses.
In addition, we have emphasized the importance of joining the FreeBSD community, which is a great resource for information, support, and collaboration. By getting involved in the community, you will have the opportunity to learn new skills, connect with other users, and contribute to the development and success of the operating system.
In conclusion, we hope this article has been helpful in getting you started with FreeBSD. We encourage you to continue exploring all that FreeBSD has to offer and take advantage of the wealth of resources and support available in the community. Good luck and happy computing!
Advertisement below